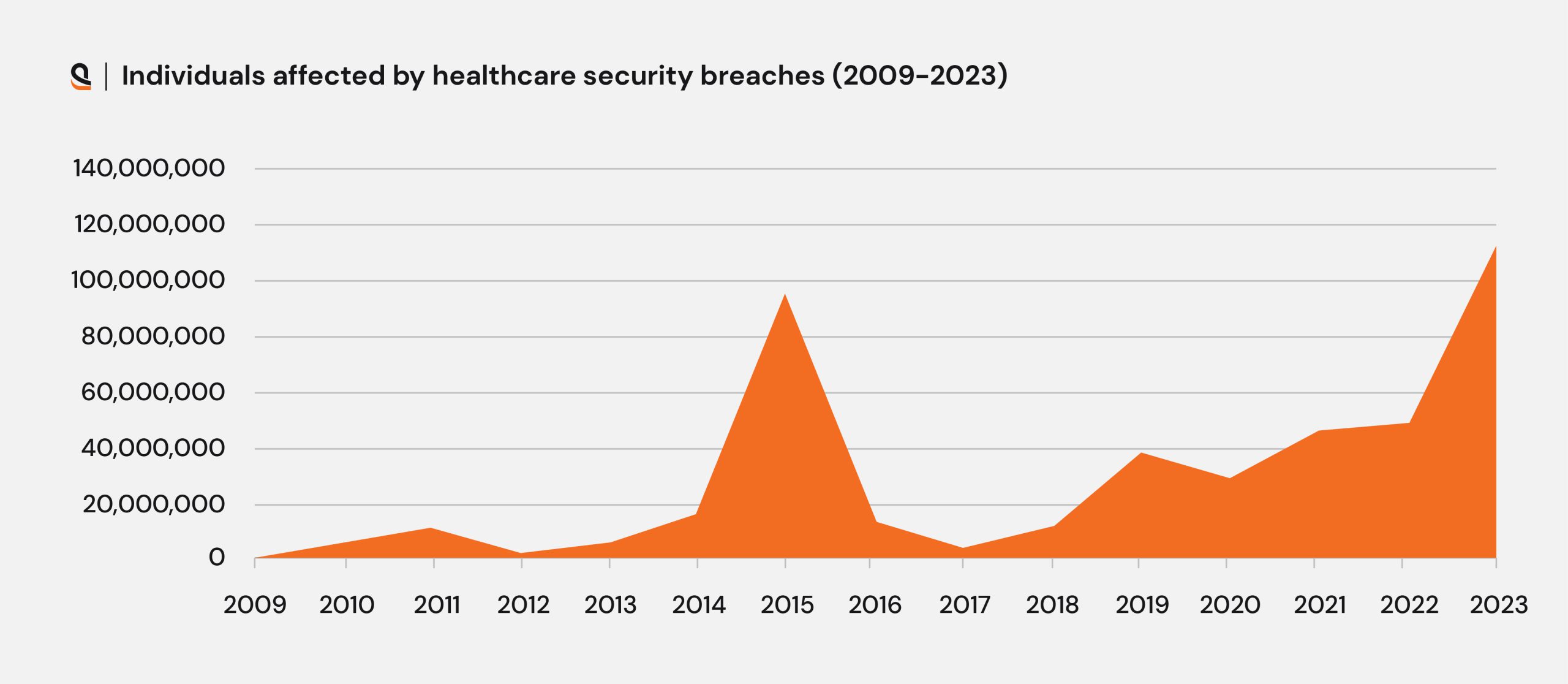
Data privacy in healthcare has undergone a big shift post-COVID-19 pandemic. With a shift in focus from clinical visits to online transactions and interactions, a large amount of private data was uploaded on-site, to the cloud, and /or to third-party systems. Data protection in healthcare has become increasingly critical as information sharing becomes more available online and data exchanges become digitalized.
As of now, roughly 36% of the world’s data volume is produced by the health sector. According to a survey, the global healthcare data interoperability market is estimated to reach USD 4.5 billion by 2026 with a growth rate of 12.9% CAGR. These data indicate the future demand and need for stringent data privacy strategies, technologies, and regulations to keep sensitive healthcare data safe and secure.
The digital healthcare sector has also been growing rapidly and its demand has been ever-increasing. While such advancements offer a variety of positive outcomes in healthcare contexts, not least for patients and employees, they also create a situation where healthcare organizations are now prime targets for malicious attackers seeking to compromise systems, ex-filtrate and sell patient data, and disrupt the industry.
The cybersecurity and privacy of patient data in healthcare include more than the HIPAA regulatory concerns. Digital solution providers are coming up with new innovative data privacy solutions and strategies to fortify the data security of patients.
Benefits of Digitization of the Healthcare Sector
Enhanced Accessibility and Efficiency – With electronic health records (EHRs), patient data is now more accessible to authorized personnel, reducing administrative delays and improving decision-making.
Improvement in Patient Care – Digitalized health systems help in the sharing of patient records which facilitates appropriate and organized care across various departments.
Cost-cutting – Digitization reduces operational overheads for healthcare providers by automating all administrative work and simplifying the process.
Data-Driven Insights – Advanced analytics tools, powered by AI-Driven Data Solutions can can process vast amounts of healthcare data, providing actionable insights for better patient outcomes and operational efficiency.
Telemedicine – Digital platforms have paved the way for online consultations and monitoring of patients making healthcare services reach the remotest areas.
All these advances have really improved the services for patients in the healthcare industry, but data privacy remains a big challenge as far as regulatory compliance and the protection of the health data of patients are concerned.
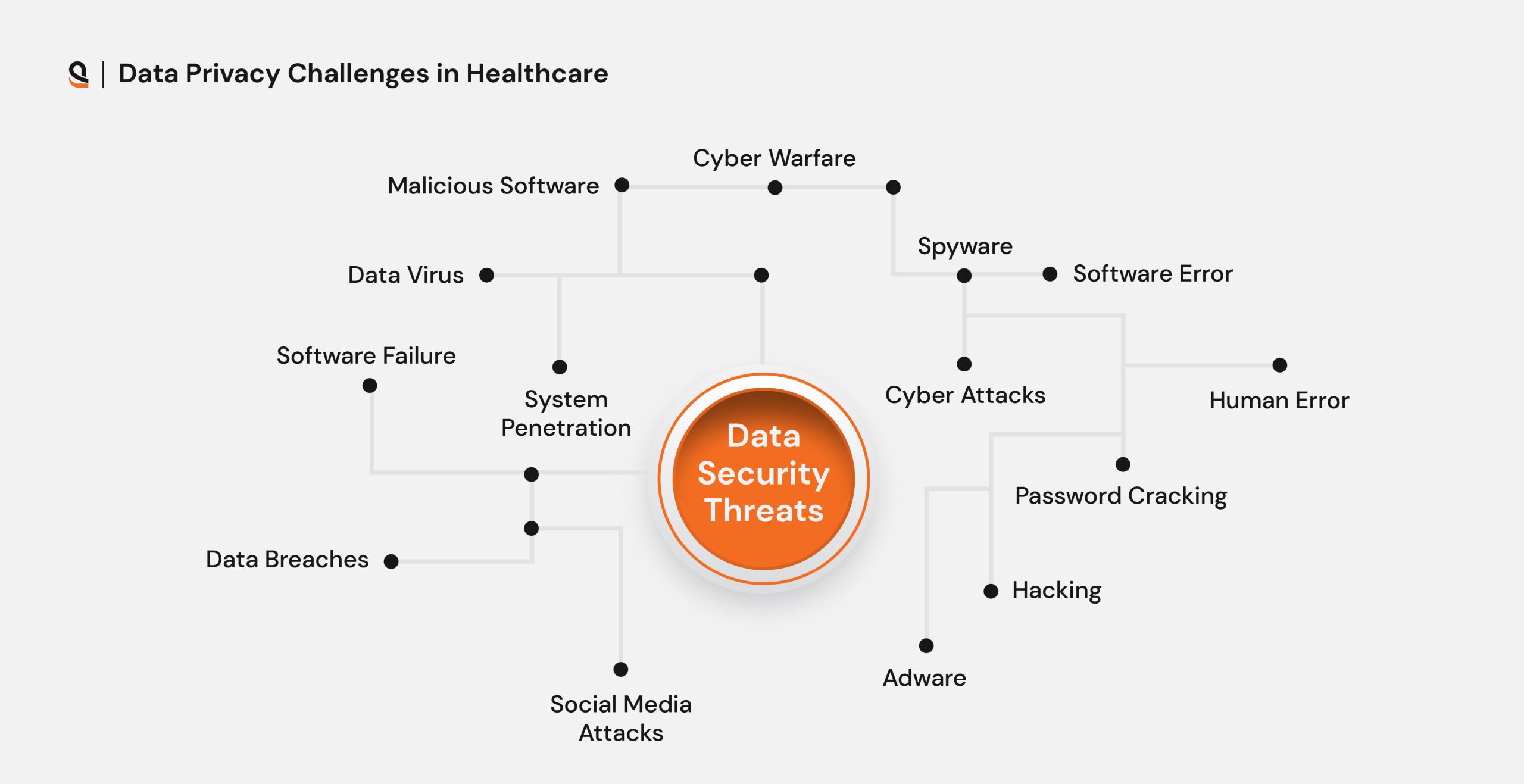
Data Privacy Challenges in Healthcare
Ransomware Attacks
A significant number of healthcare organizations have suffered ransomware attacks with the rise of digital healthcare services. More than half of the healthcare organizations have experienced data breaches. Healthcare data is always on priority for cyber attackers highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Unsecured Mobile Applications
The rise of telehealth exposed sensitive data through mobile apps lacking advanced security. Developers are now focusing on strengthening app security to mitigate these risks.
Reduced Interoperability
Limited interoperability between various electronic health record (EHR) systems causes errors, delays, and data exposure. Disjointed systems and duplicated data across platforms exacerbate vulnerabilities, requiring IT teams to address compatibility issues to protect patient data.
Vulnerabilities in the Internet of Things (IoT)
The development of IoT has improved healthcare’s operational efficiency, but it has also brought additional security risks. Most unmanaged IoT devices lack a standard security measure, which increases the chances of data breaches and greatly jeopardizes healthcare data privacy.
Limitations in Resources
Many organizations in the Healthcare Industry have under-staffed, unskilled, or under-funded resources, making it hard for them to respond to the threat of cyber attacks. It is necessary to educate broader sections and invest more in these advanced technologies to fill those gaps and find potential solutions to the data privacy challenges.
Improving healthcare data security in the Healthcare Industry requires addressing these challenges through better resources, enhanced interoperability, and the adoption of advanced cybersecurity measures.
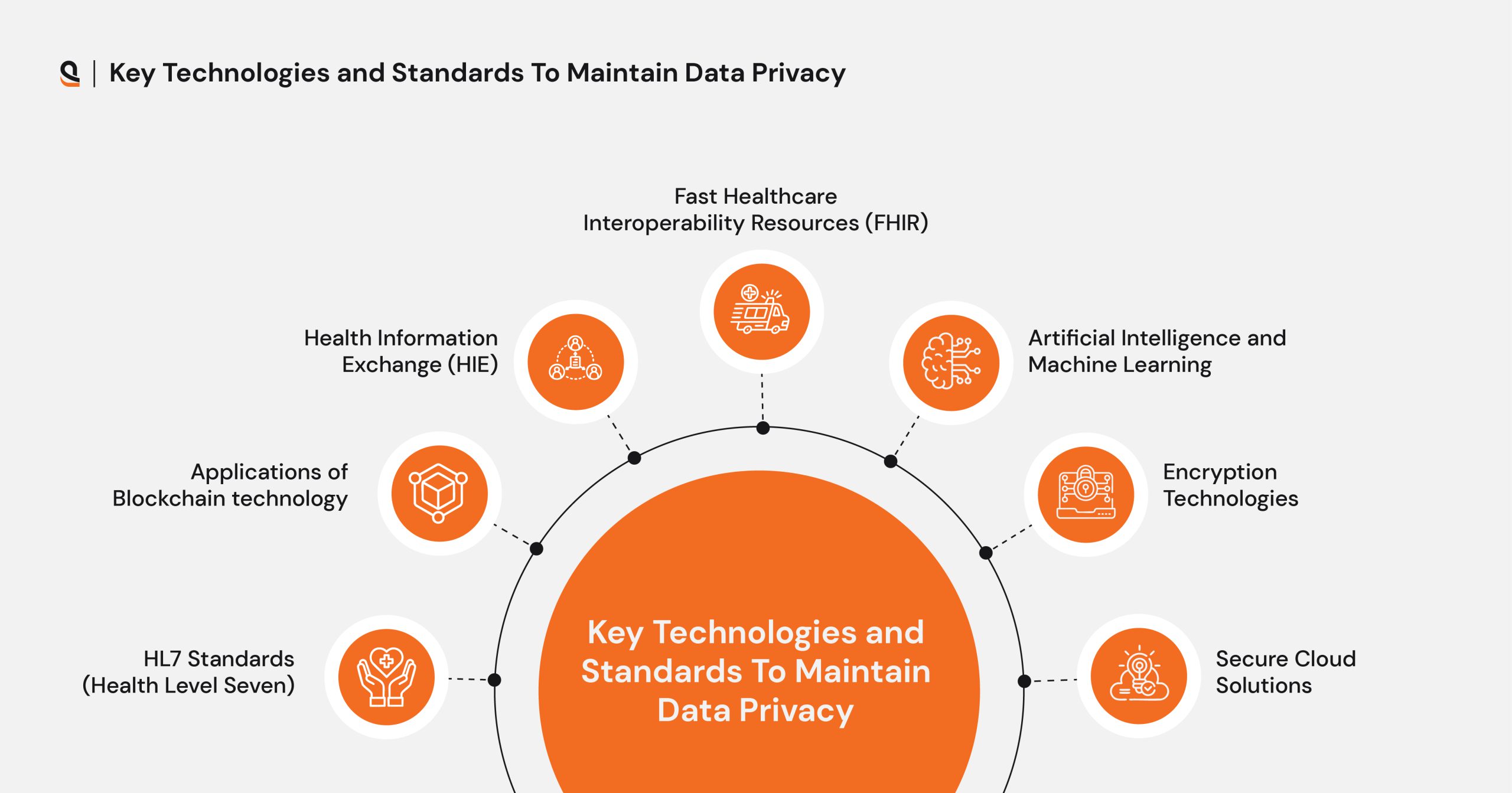
Key Technologies and Standards To Maintain Data Privacy
The technologies and standards listed below help in securing the sensitive data of patients and healthcare organizations.
HL7 Standards (Health Level Seven)
HL7 is a set of international standards for transferring, integrating, and retrieving electronic health information. These standards provide a framework to improve interoperability between healthcare systems, ensuring secure and seamless data exchange. HL7 fosters data integrity and privacy by specifying how sensitive patient information is structured, stored, and shared, reducing vulnerabilities. For example, HL7’s Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) standardizes clinical documentation formats, enabling secure and accurate sharing among providers.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchains are decentralized ledger transactions that record but do not modify or destroy any transaction associated with a record. Blockchain can be applied in healthcare to:
- Encrypt patient records using cryptographic hashing.
- Allow patients to govern data access directly managing the permissions on the blockchain.
- Increase interoperability by creating a single platform for data sharing between providers.
- Decentralizing those functions reduces the risk associated with unauthorized access, tampering, or loss of data.
Health Information Exchange (HIE)
HIE provides for the electronic transformation or movement of health information among organizations. It enables improved coordination and care by ensuring that patient information is available whenever required but restricting who can access it. Most HIEs use strong encryption and authentication protocols to ensure that sensitive information is safe during exchange and while stored in either location. HIE enhances compliance with data privacy regulations by augmenting auditable trails of information access and sharing.
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR)
FHIR is a standard developed by HL7 to facilitate the exchange of healthcare information across systems. Its features include:
- Interoperability: Allowing disparate systems to communicate with one another through standard APIs.
- Data privacy and Security: It has incorporated more enhanced security protocols like OAuth2 and SMART on FHIR to better secure access to and sharing of patient data.
- Patient Empowerment: Granting permission to patients to access their health data and be in control over it directly.
FHIR supports modern healthcare applications, making data more accessible while prioritizing security and privacy.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML are important in the areas of health data privacy because:
- Threat Detection: They enable the identification of unusual patterns or anomalies in data access because of which a potential breach may occur.
- Predictive Analytics: The technology attempts to identify the vulnerabilities and act beforehand.
- De-identification of data: Automatic anonymization of the personal information in research data sets is performed to secure patient privacy.
These technologies streamline the detection and prevention of potential data security risks, enhancing overall data protection.
Encryption Technologies
Encryption ensures that sensitive data remains secure by converting it into unreadable formats that require specific keys for decryption. Key encryption methods include:
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is used to safeguard saved and transmitted data.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is used to secure communication within healthcare providers.
- Homomorphic Encryption, allows computations while keeping the encrypted data without decrypting it.
Encryption is necessary to keep patient information secure both when it is moving through and when it is stored, and is one area, among many, whereby compliance is required to meet, such as HIPAA.
Secure Cloud Solutions
These platforms have scalable and secure environments for storing and processing healthcare data. The cloud platforms incorporate different types of measures, such as:
- End-to-End Encryption: To ensure that the data is encrypted during storage and between storage and the end user.
- Access Control Mechanisms: Restricting data access to authorized personnel only.
- Privacy-Preserving Technologies: Using techniques like differential privacy to protect patient data while enabling its analysis.
Providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure have designed healthcare-specific solutions with compliance certifications inclusive of the ones implemented (like HIPAA, and GDPR).
Strategies to Secure Data Privacy in Digital Healthcare
To address these challenges, healthcare organizations must adopt robust data privacy strategies like:
Implementation of Advanced Access Controls: Utilizing role-based access controls and authentication methods like OAuth 2.0 ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit protects it from unauthorized access during transmission or storage.
- Regular Auditing and Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of data access logs and periodic audits help detect and respond to potential threats in real time.
- Compliance with Global Standards: Aligning with frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA ensures adherence to legal requirements and bolsters patient trust.
- Cybersecurity Layer Integration: Add an additional layer of protection against cyberattacks by employing advanced cybersecurity measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and anti-malware solutions.
Conclusion
The digitization of the healthcare sector facilitated interconnected systems creating huge data. Advanced technologies and strategies prioritizing data privacy provide interoperability between disparate systems along with benefits such as enhanced security and scalability for smoother data exchange and better patient care. Curb unauthorized access, data interception, data integrity, and third-party risks with our data privacy solution tailored specially for the healthcare industry.
AQe Digital can help secure your healthcare data and deliver better patient care by leveraging cutting-edge technologies and industry best practices.